Volume 14, Issue 3 (September 2017)
Abstract
(29371 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(7010 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
Highlights
- Different polymeric nanocomposite materials for bumper beam were injection molded.
- Criteria weighting was carried out through AHP and Entropy methods.
- Material selection was performed using TOPSIS and MOORA methods.
- Impact and tensile strengths were the most important criteria.
- PC/ 0.5 wt% nano Al2O3 is the most appropriate material for automotive bumper beam.
Abstract
(38054 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6430 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
- In this study the use titanium and tungsten as alternatives to the noble metals in the jewellery industry was investigated.
- Alternate immersion tests were performed in 3.5% sodium chloride and artificial perspiration. The metals’ abrasion resistance with respect to textile fabrics was determined.
- In general, there is around 30% difference in pit density for titanium and tungsten as compared to that of gold. Pit depth and pit diameter showed a similar trend.
- It was found that if titanium and tungsten would be used to manufacture jewellery products, they would have longer maintenance intervals than that of gold.
- New tools and techniques, however, would be required by jewellers to work with titanium and tungsten.
Abstract
(30166 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6206 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
- The use of short heat treatment cycles to reduce the diffusion of oxygen into the titanium alloy
- Improvement of wear resistance of Ti-grade 5 alloy by changing the microstructure via heat treatment
- Determination of wear micro-mechanism of Ti-grade 5 alloy
Abstract
(25115 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6734 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
- Oxide films, intentionally created in Zn4Al and ZA27 by the OMO sandwich method, were studied.
- The thickness of the oxide films in Zn4Al and ZA27 alloys, based on halving the thickness of a fold, is estimated to be within the range of 70-200 nm and 30-100 nm, respectively.
- Thermodynamic examinations showed that the most stable oxide phase, on the surface of the Zn4Al and ZA27 alloys, is the aluminum oxide.
- The thickness of the oxide films through kinetic considerations were identical and estimated to be in the range of 2-5 nm, showing the intense effect of turbulent melt flow on the oxidation behavior of cast alloys.
Abstract
(25029 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6487 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
- Multilayered Ag6Mo10O33 and Ni-substituted one were prepared by mechanochemical.
- Acetamide as driving agent directed solid reaction towards producing rod structure.
- Image processing program showed average diameter of 92 nm for Ag6Mo10O33.
- The partial substitution of Ag+ by nickel unit decreased particle size to 87 nm.
- Ni-substituted sample indicated good photo catalytic ability in water purification.
Abstract
(27842 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6348 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
- The deep rolling process produced a ultrafine-grained layer with increased hardness on the surface of the AISI 316L stainless steel.
- The plasma nitriding at the used conditions generated a hard nitrided layer with further hardness than the deep rolling.
- Deep rolling process combined with plasma nitriding created a thicker nitrided layer with more hardness due to the increased diffusional rapid channels.
- Un-lubricated wear resistance was improved by both the processes particular the plasma nitriding
- Wear resistance at the combined status was found better than the individually processed conditions
Abstract
(26905 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6378 Downloads)
Abstract
(28977 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(6597 Downloads)
|
Graphical Abstract
|
Highlights
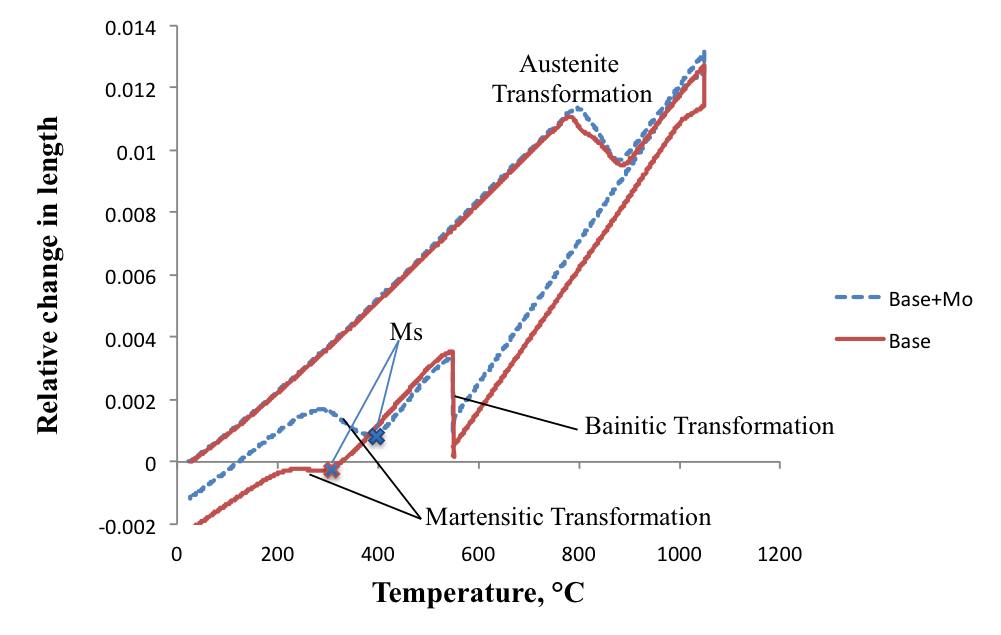
- Mo retards the bainitic transformation and enhances the hardenability of the steel.
- Mo leads to higher fraction of martensite after cooling from isothermal temperature.
- Bainitic microstructure was obtained in the air-cooled Mo-added steel.
- Mechanical properties of the microalloyed steel are improved by Mo addition.
Export as:
HTML
|
XML
|
RSS

 , H. Rashvand
, H. Rashvand 
 , Sh. Raygan
, Sh. Raygan 
 , J. Rassizadehghani
, J. Rassizadehghani 
 , Y. Palizdar
, Y. Palizdar 
 , C. Garcia Mateo
, C. Garcia Mateo 
 , D. San Martin
, D. San Martin 


 , H. Rashvand
, H. Rashvand 
 , Sh. Raygan
, Sh. Raygan 
 , J. Rassizadehghani
, J. Rassizadehghani 
 , Y. Palizdar
, Y. Palizdar 
 , C. Garcia Mateo
, C. Garcia Mateo 
 , D. San Martin
, D. San Martin